Metal Debugger#
Profiling is a key step for performance optimization. You can build MLX with
the MLX_METAL_DEBUG option to improve the Metal debugging and
optimization workflow. The MLX_METAL_DEBUG debug option:
Records source during Metal compilation, for later inspection while debugging.
Labels Metal objects such as command queues, improving capture readability.
To build with debugging enabled in Python prepend
CMAKE_ARGS="-DMLX_METAL_DEBUG=ON" to the build call.
The metal.start_capture() function initiates a capture of all MLX GPU
work.
Note
To capture a GPU trace you must run the application with
MTL_CAPTURE_ENABLED=1.
import mlx.core as mx
a = mx.random.uniform(shape=(512, 512))
b = mx.random.uniform(shape=(512, 512))
mx.eval(a, b)
trace_file = "mlx_trace.gputrace"
# Make sure to run with MTL_CAPTURE_ENABLED=1 and
# that the path trace_file does not already exist.
mx.metal.start_capture(trace_file)
for _ in range(10):
mx.eval(mx.add(a, b))
mx.metal.stop_capture()
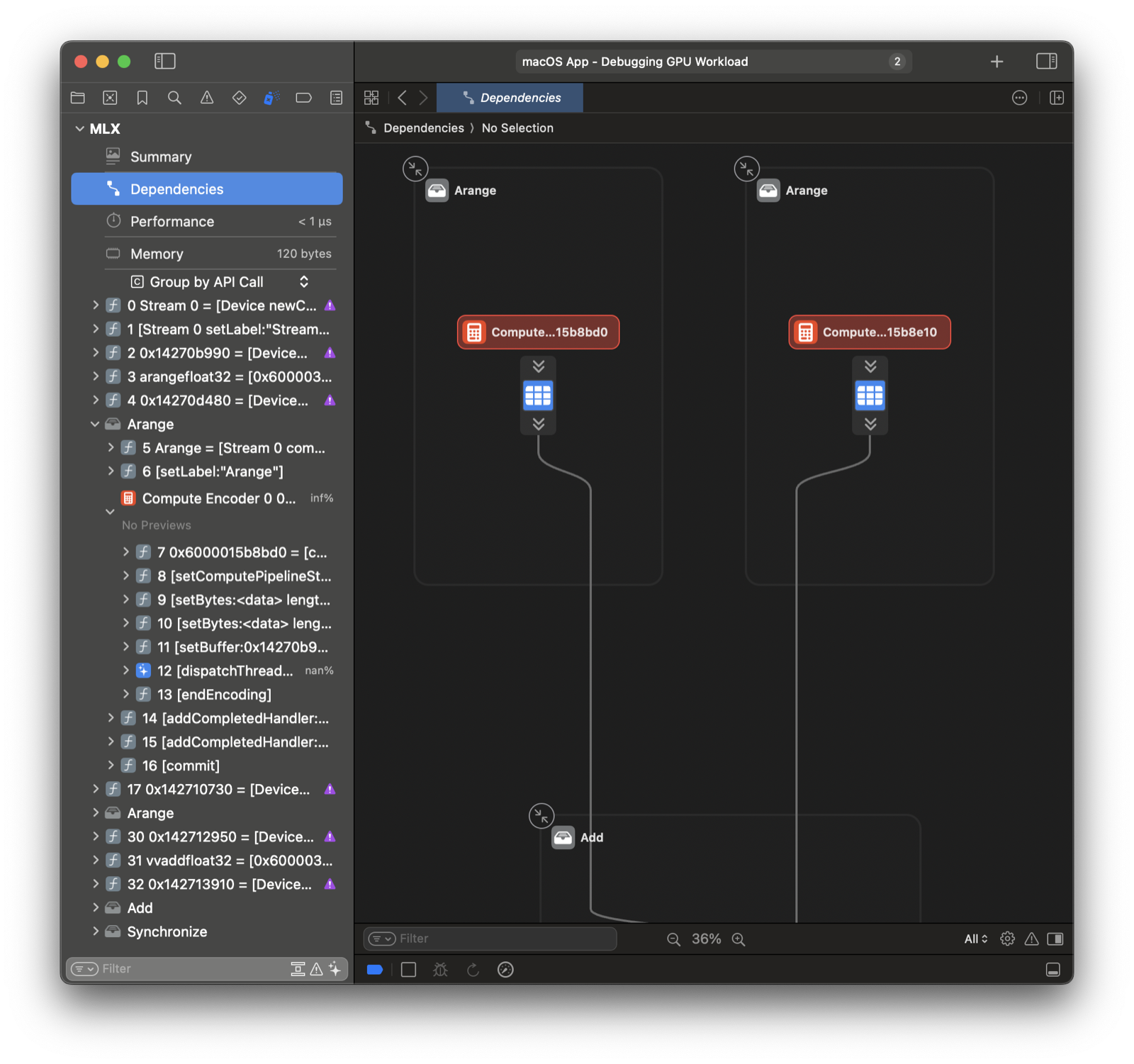
You can open and replay the GPU trace in Xcode. The Dependencies view
has a great overview of all operations. Checkout the Metal debugger
documentation for more information.
Xcode Workflow#
You can skip saving to a path by running within Xcode. First, generate an Xcode project using CMake.
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DMLX_METAL_DEBUG=ON -G Xcode
open mlx.xcodeproj
Select the metal_capture example schema and run.